Photovoltaic solar cells, also known as solar panels, are a crucial component of renewable energy systems. They work by converting sunlight into electricity, and are widely used to power homes, businesses, and even entire communities. But how are these important devices actually made? In this article, we’ll explore the process of creating photovoltaic solar cells from start to finish.
The Basics of Photovoltaic Solar Cells
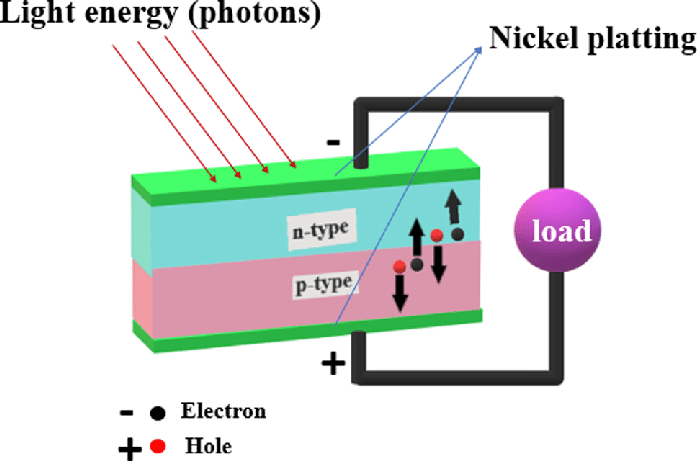
Before we dive into the manufacturing process, let’s first understand the basics of photovoltaic solar cells. These cells are typically made from silicon, a widely available and affordable semiconductor material. When light hits the surface of a solar cell, it knocks electrons loose from the silicon atoms, creating an electric current. This current can then be harnessed to power electrical devices or be stored for later use.Step 1: Silicon Ingot Production
The production of photovoltaic solar cells begins with the creation of silicon ingots. These ingots are made through a process called “Czochralski pulling,” where a seed crystal of silicon is dipped into a vat of molten silicon and slowly pulled upwards. As the crystal is pulled, it causes the molten silicon to solidify and form a large, single crystal ingot.Step 2: Wafer Production
Once the silicon ingots are created, they are sliced into thin wafers using a diamond wire saw. These wafers are then polished to remove any imperfections and create a smooth, flat surface. The wafers are typically very thin, usually around 200 micrometers thick, and can be either monocrystalline or polycrystalline, depending on the manufacturing process used.

