How Do Photovoltaic Cells Work for Dummies

Understanding the Basics of Photovoltaic Cells
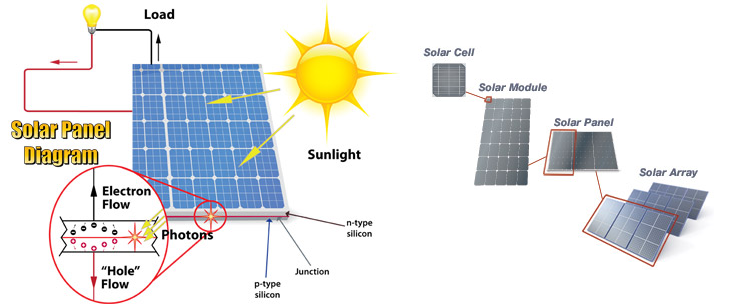
Photovoltaic cells, also known as solar cells, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. These cells are made from semiconductor materials, such as silicon, which can absorb photons of light and release electrons. When photons from the sun strike the surface of the cell, they dislodge electrons from the atoms within the semiconductor material, creating an electric current. This can then be harnessed and used to power electrical devices.The Function of Photovoltaic Cells
The process of converting sunlight into electricity begins with the absorption of photons by the photovoltaic cell. The photons transfer their energy to the electrons in the semiconductor material, allowing them to move freely. This creates a flow of electrons, or an electric current, within the cell. The electric current is then collected and channeled through an external circuit, where it can be used to power devices or stored in a battery for later use.Types of Photovoltaic Cells
There are several types of photovoltaic cells, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. The most common type is the crystalline silicon cell, which is widely used in rooftop solar panels and large-scale solar farms. Other types include thin-film solar cells, which are lightweight and flexible, making them suitable for portable electronic devices, and multi-junction cells, which are highly efficient and often used in space applications.