How Photovoltaic Power Works
Understanding Photovoltaic Power
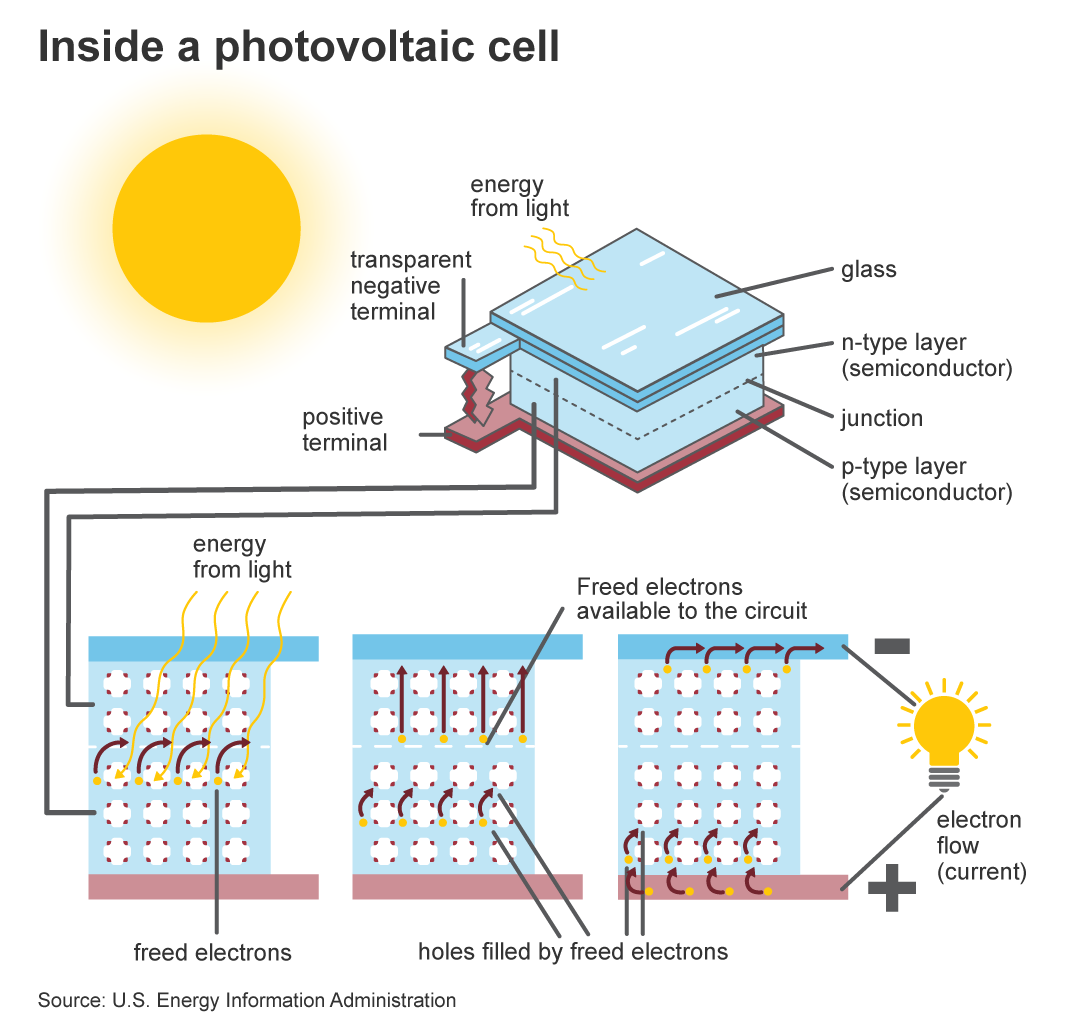
Photovoltaic power, also known as solar power, is a renewable energy source that converts sunlight into electricity. It is generated by using photovoltaic cells, which are made of semiconductor materials like silicon. When sunlight hits these cells, it creates an electric current, which can then be converted into usable power for homes, businesses, and other applications.The Basic Process
The basic process of photovoltaic power generation starts with the photovoltaic cells absorbing sunlight. When sunlight strikes the cells, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material, creating a flow of electric current. This direct current (DC) is then passed through an inverter, which converts it into alternating current (AC), the type of electricity used to power homes and businesses.System Components
In addition to the photovoltaic cells and the inverter, a photovoltaic power system includes other components such as mounting hardware, wiring, and a power meter. The mounting hardware is used to secure the photovoltaic panels in place, typically on the roof of a building or on the ground. The wiring connects the panels to the inverter and then to the electrical panel of the building. The power meter measures the amount of electricity generated by the photovoltaic system.

