The Photovoltaic Effect: Harnessing the Power of Solar Energy
The Basics of the Photovoltaic Effect
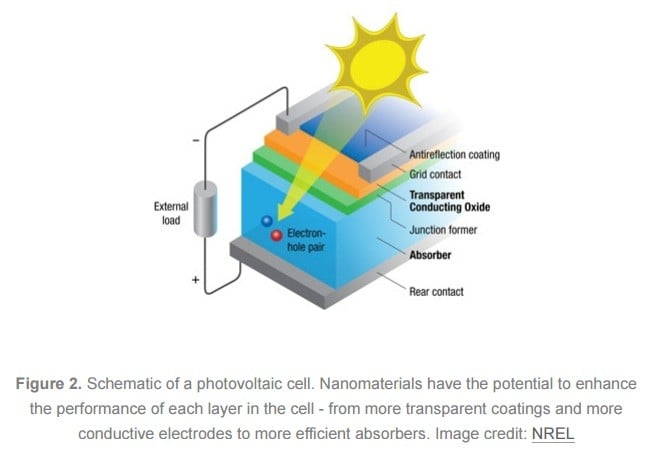
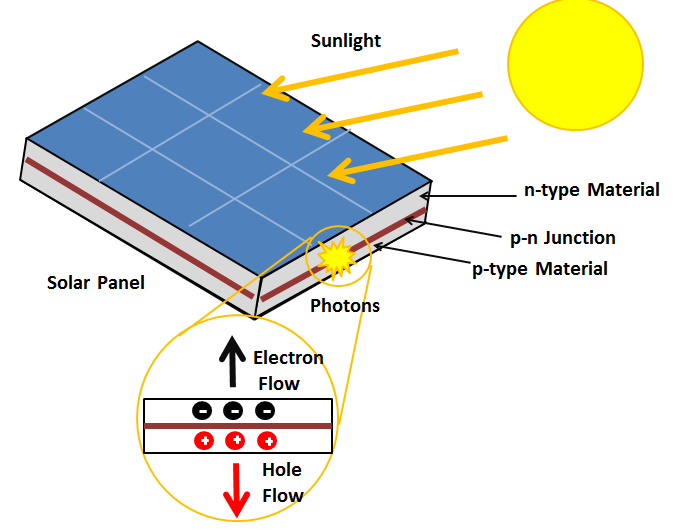
The photovoltaic effect is the process by which sunlight is converted into electricity. This phenomenon occurs when certain materials, known as semiconductors, absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons, creating an electric current. The most common and widely used semiconductor for this purpose is silicon, but other materials such as cadmium telluride and copper indium gallium selenide are also used in photovoltaic cells.How Photovoltaic Cells Work
When sunlight strikes a photovoltaic cell, it excites the electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to break free from their atoms. The movement of these free electrons generates an electric current, which can then be harnessed to power electrical devices. This electricity can be used immediately, stored in batteries for later use, or fed into a grid for distribution to consumers.The Importance of the Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect plays a crucial role in the field of renewable energy, as it allows for the direct conversion of sunlight into electricity without the need for any moving parts or fuel. This makes photovoltaic cells an ideal source of clean, sustainable energy, particularly in areas with abundant sunlight.