The photovoltaic effect in solar cells is a process converts sunlight into electricity. This phenomenon was first discovered by Alexandre-Edmond Becquerel in 1839 and has since been harnessed to produce clean, renewable energy. In this article, we will explore the photovoltaic effect in detail and how it is utilized in solar cells to generate electricity.
The Photovoltaic Effect
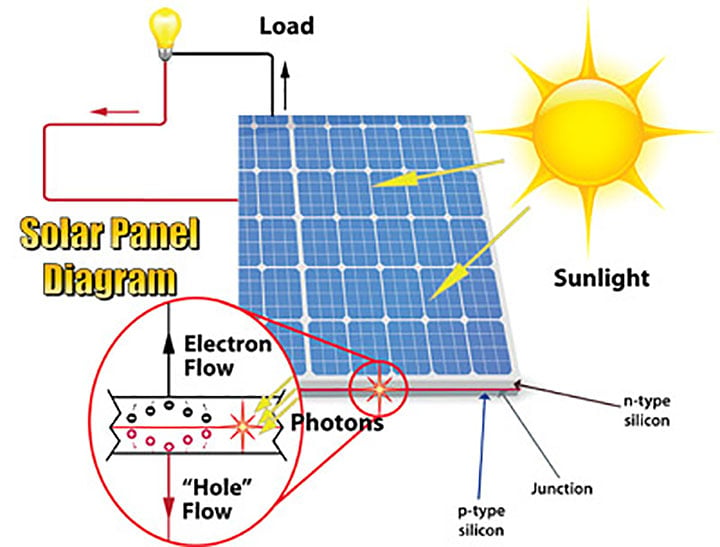
The photovoltaic effect occurs when photons from sunlight are absorbed by a material, such as silicon, and release electrons. This creates an electric current, which can then be harnessed to power electrical devices. The process relies on the properties of certain materials, known as semiconductors, which have the ability to convert light energy into electrical energy.How Solar Cells Work
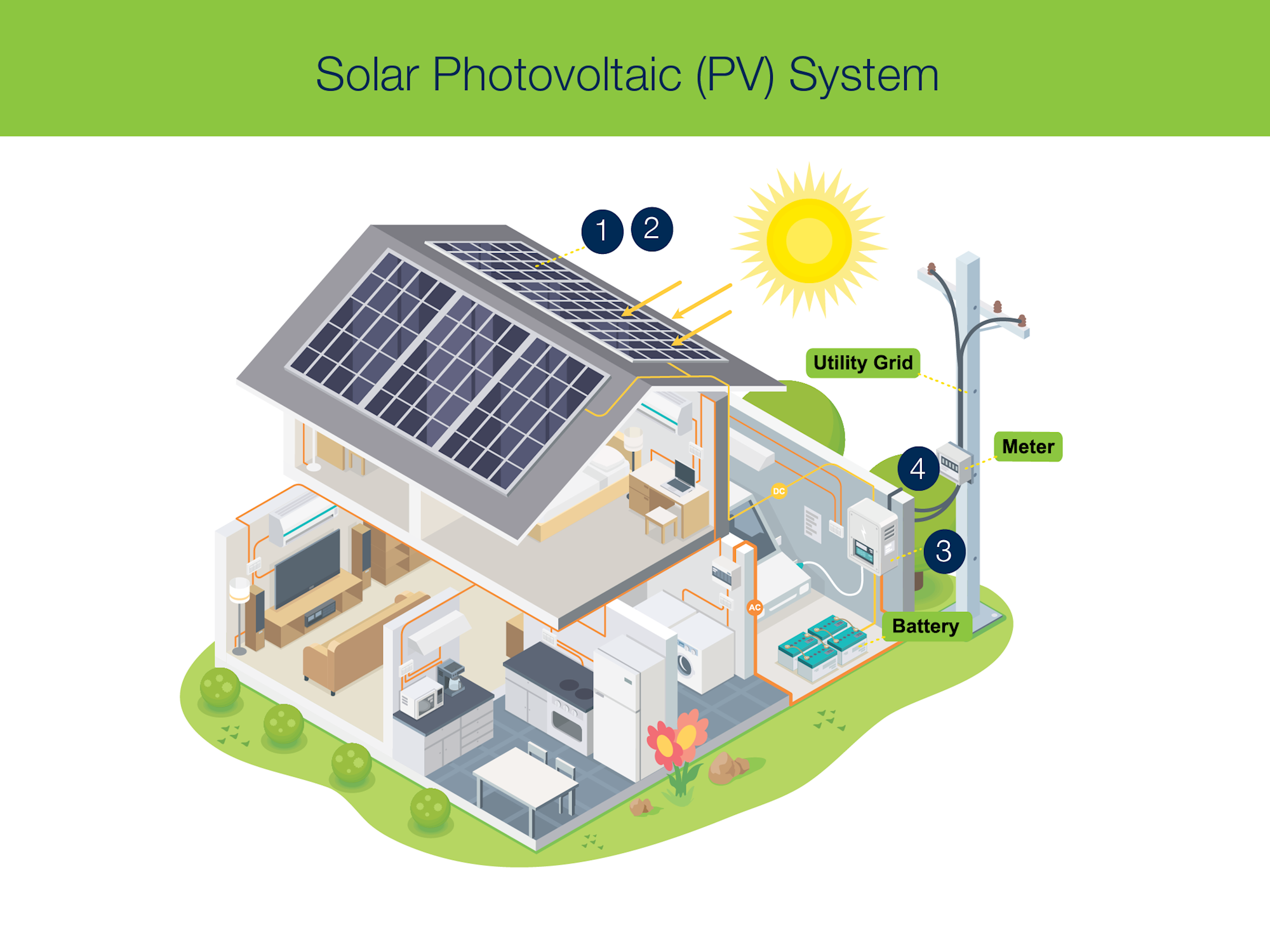
Solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, are the building blocks of solar panels. They consist of layers of semiconductor material, usually silicon, which are treated to create an electric field. When sunlight strikes the solar cell, the photons are absorbed and create an electric current. This current is then collected and transferred to an external circuit, where it can be used to power electrical devices.Types of Solar Cells
There are several different types of solar cells, each with their own unique properties and efficiencies. These include monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film solar cells. Each type of solar cell utilizes the photovoltaic effect to generate electricity, but they differ in terms of cost, efficiency, and production processes.